Minimizing online risks for maximum security
Privacy at the core
Our commitment is to provide security tools that are simple to use yet powerful enough to defend against ever-evolving cyber threats.

Minimizing online risks for maximum security
Privacy at the core
Our commitment is to provide security tools that are simple to use yet powerful enough to defend against ever-evolving cyber threats.

The Tech Behind Our Security
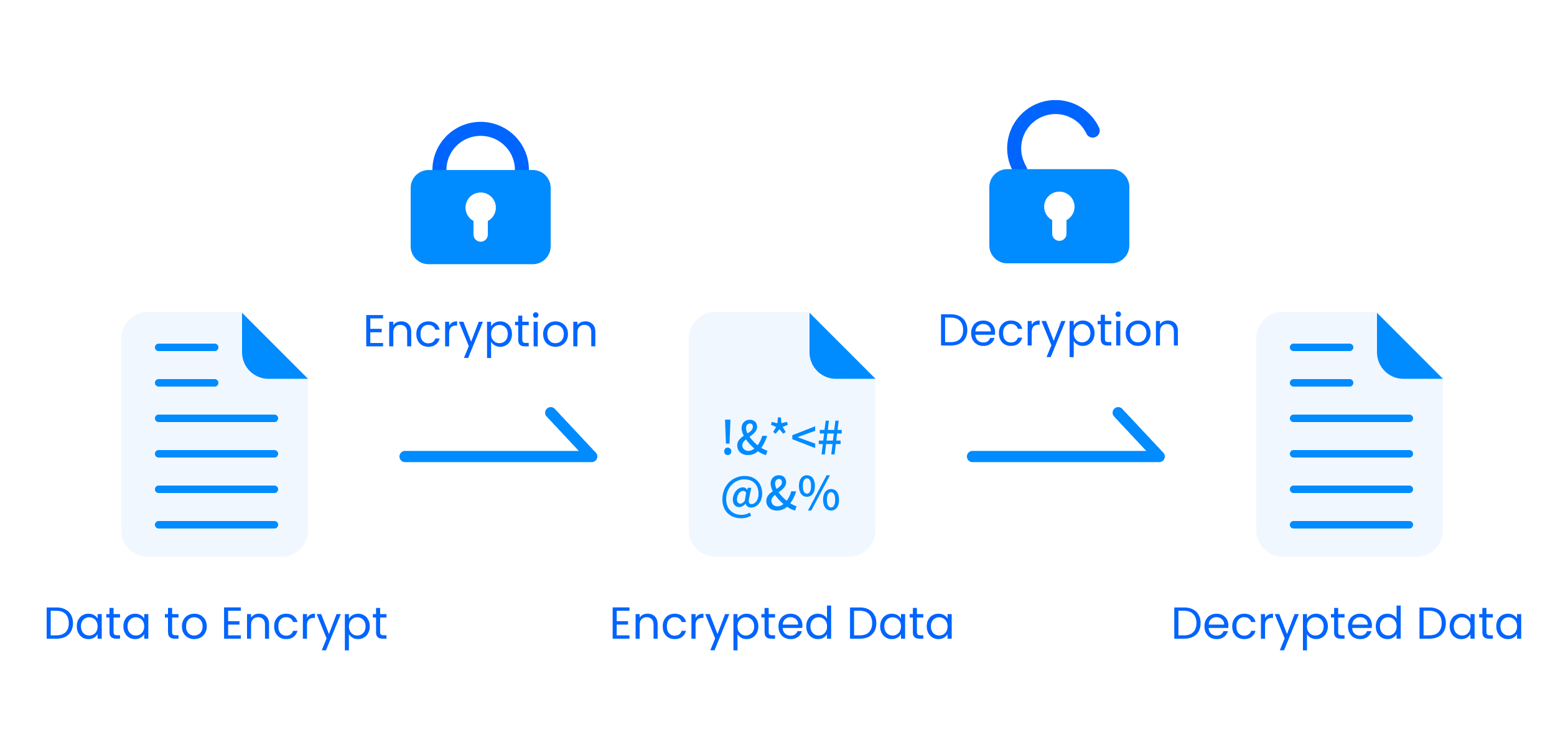
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a widely used encryption algorithm, recognized for its high level of security. The 256-bit version is one of the strongest, making it virtually impossible to crack due to the vast number of possible key combinations. It encrypts data into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted with the correct key.
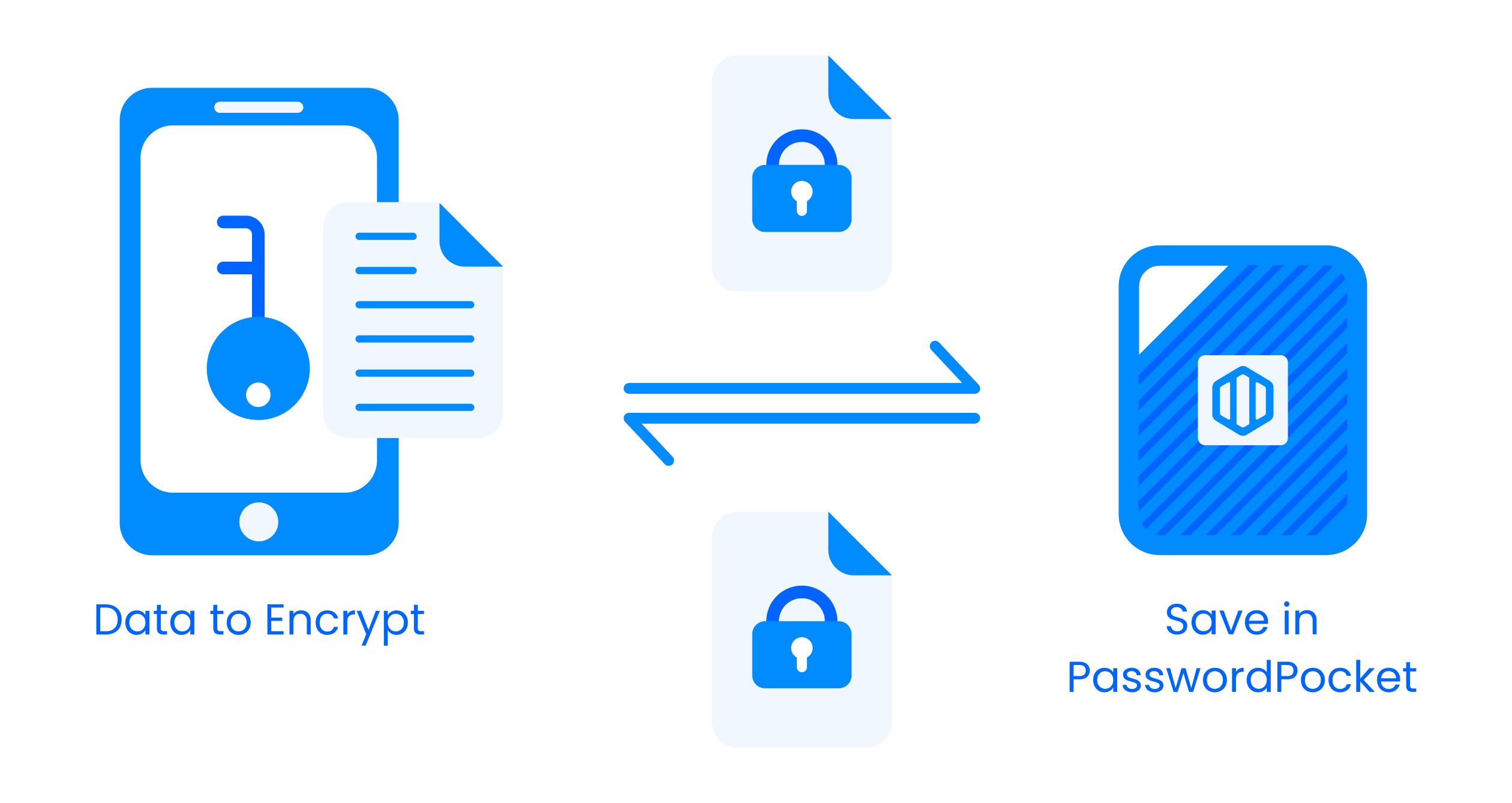
This ensures that only the communicating users can read the messages, with the encryption being done at the sender’s device and decrypted at the recipient's. No one in between, including service providers, can access the encrypted data. Guaranteeing absolute protection against interception during transmission.
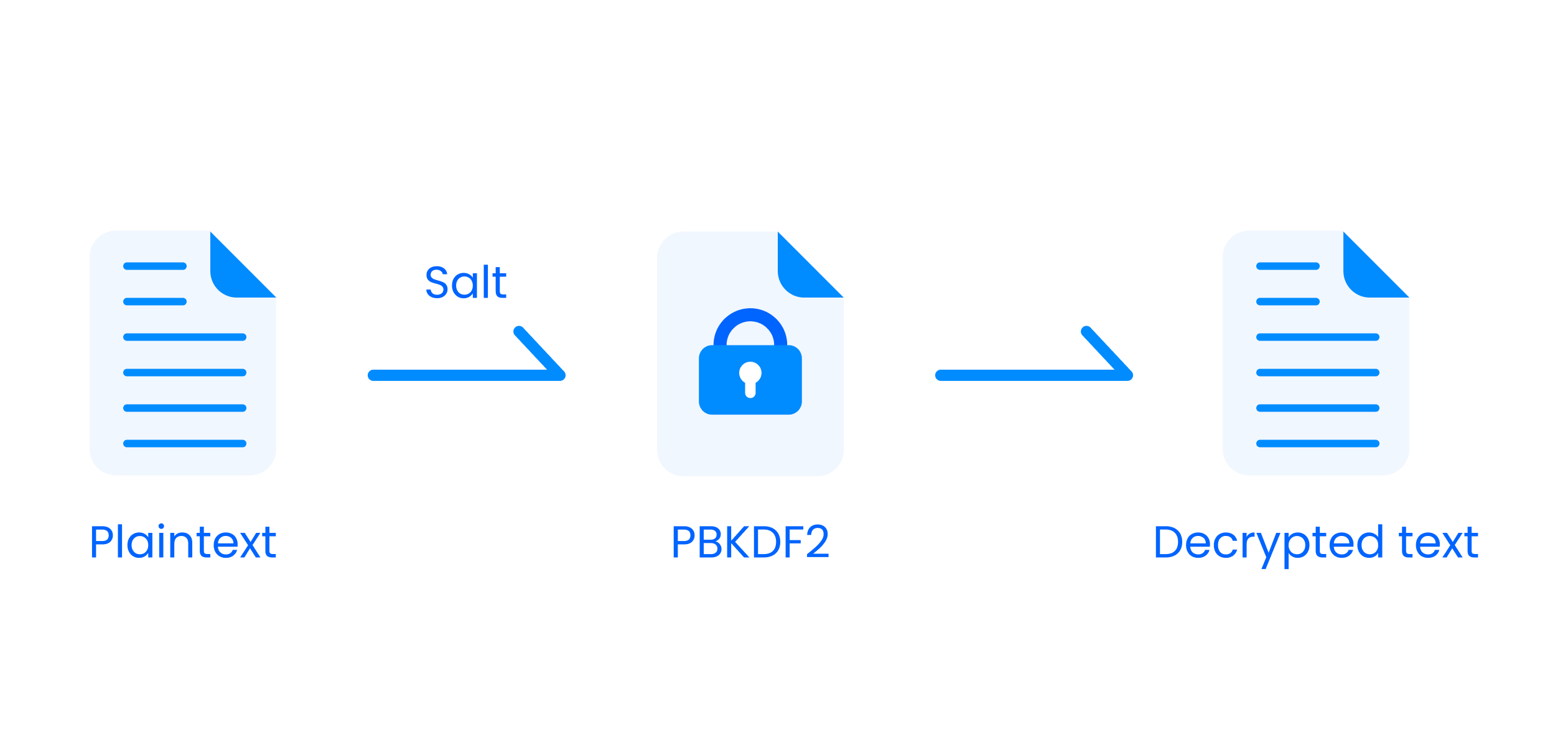
PBKDF2 is a cryptographic function used to derive a secure encryption key from a password. It adds "salt" (random data) and iterates the process thousands of times to make it much harder for attackers to crack the password using brute force. By enhancing the complexity of password hashing, PBKDF2 significantly strengthens password protection in databases.